[ad_1]
Utilizing machine studying and scientific knowledge from digital well being data, researchers on the Icahn College of Drugs at Mount Sinai in New York constructed an in silico, or computer-derived, marker for coronary artery illness (CAD) to higher measure clinically essential characterizations of the illness.
The findings, revealed on-line on December 20 in The Lancet, might result in extra focused prognosis and higher illness administration of CAD, the most typical kind of coronary heart illness and a number one reason for dying worldwide. The examine is the primary recognized analysis to map traits of CAD on a spectrum. Earlier research have centered solely on whether or not or not a affected person has CAD.
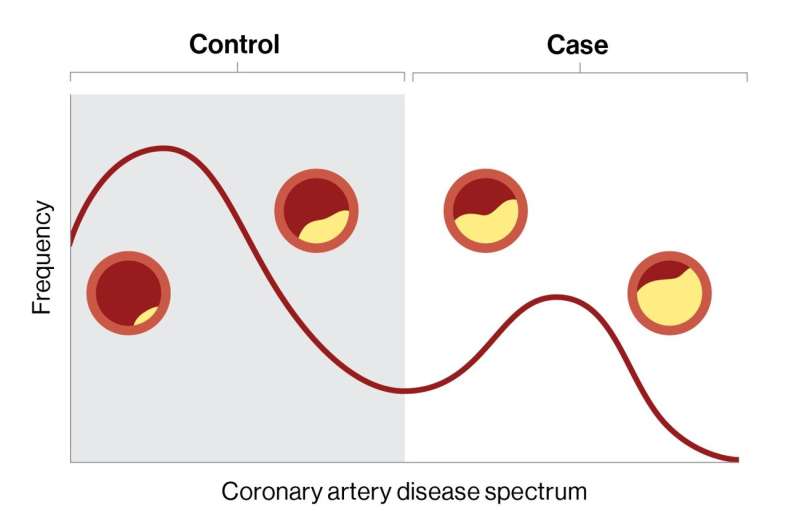
CAD and different frequent situations exist on a spectrum of illness; every particular person’s mixture of danger elements and illness processes determines the place they fall on the spectrum. Nevertheless, most such research break this illness spectrum into inflexible courses of case (affected person has illness) or management (affected person doesn’t have illness). This may occasionally lead to missed diagnoses, inappropriate administration, and poorer scientific outcomes, say the investigators.
“The data gained from this non-invasive staging of illness may empower clinicians by extra precisely assessing affected person standing and, subsequently, inform the event of extra focused remedy plans,” says Ron Do, Ph.D., senior examine creator and the Charles Bronfman Professor in Personalised Drugs on the Icahn College of Drugs at Mount Sinai.
“Our mannequin delineates coronary artery illness affected person populations on a illness spectrum; this might present extra insights into illness development and the way these affected will reply to remedy. Being able to disclose distinct gradations of illness danger, atherosclerosis, and survival, for instance, which can in any other case be missed with a standard binary framework, is essential.”
Within the retrospective examine, the researchers educated the machine studying mannequin, named in silico rating for coronary artery illness or ISCAD, to precisely measure CAD on a spectrum utilizing greater than 80,000 digital well being data from two giant well being system-based biobanks, the BioMe Biobank on the Mount Sinai Well being System and the UK Biobank.
The mannequin, which the researchers termed a “digital marker,” included lots of of various scientific options from the digital well being report, together with very important indicators, laboratory take a look at outcomes, drugs, signs, and diagnoses, and in contrast it to each an present scientific rating for CAD, which makes use of solely a small variety of predetermined options, and a genetic rating for CAD.
The 95,935 individuals included individuals of African, Hispanic/Latino, Asian, and European ethnicities, in addition to a big share of girls. Most scientific and machine studying research on CAD have centered on white European ethnicity.
The investigators discovered that the chances from the mannequin precisely tracked the diploma of narrowing of coronary arteries (coronary stenosis), mortality, and problems resembling coronary heart assault.
“Machine studying fashions like this might additionally profit the well being care trade at giant by designing scientific trials based mostly on acceptable affected person stratification. It could additionally result in extra environment friendly data-driven individualized therapeutic methods,” says lead creator Iain S. Forrest, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow within the lab of Dr. Do and an MD/Ph.D. pupil within the Medical Scientist Coaching Program at Icahn Mount Sinai.
“Regardless of this progress, it is very important do not forget that doctor and procedure-based prognosis and administration of coronary artery illness aren’t changed by synthetic intelligence, however somewhat doubtlessly supported by ISCAD as one other highly effective software within the clinician’s toolbox.”
Subsequent, the investigators envision conducting a potential large-scale examine to additional validate the scientific utility and actionability of ISCAD, together with in different populations. Additionally they plan to evaluate a extra moveable model of the mannequin that can be utilized universally throughout well being methods.
Ben O. Petrazzini et al, Machine learning-based marker for coronary artery illness: Derivation and validation in two longitudinal cohorts, The Lancet (2022). www.thelancet.com/journals/lan … (22)02079-7/fulltext
The Mount Sinai Hospital
Quotation:
Growing a digital marker for coronary artery illness (2022, December 20)
retrieved 20 December 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2022-12-digital-marker-coronary-artery-disease.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link


